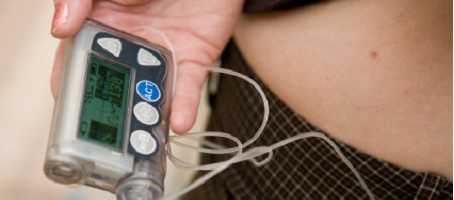
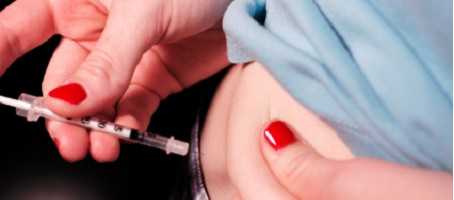
Insulin pumps appear to offer better diabetes control in people with type 2 diabetes than injections.
The OpT2mise trial, funded by insulin pump manufacturer Medtronic, was a multinational trial carried out across hospitals in Europen, Canada, USA, Israel and South Africa.
331 patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes were enrolled onto the study. The patients had previously been on multiple daily injections to control their diabetes. Average HBA1c had been 9% (75 mmol/mol) at the start of the study. Participants were randomly assigned to either continue on multiple injections per day or to move onto an insulin pump.
At 6 months participants on daily injections reduced their HbA1c by 0.4 (4 mmol/mol) whilst participants on an insulin pump reduced their HbA1c by 1.1% (12 mmol/mol). Average daily insulin dose was lower, by the end of the study for patients on a pump, taking 97 units per day compared with 122 units per day taken by participants on injections.
Whilst type 2 diabetes can usually be treated without the need for insulin, it is relatively common for people that have had type 2 diabetes for a number of years to require a number of insulin injections per day to manage their diabetes.
Currently, it is rare for insulin pumps to be used as a treatment option for people with type 2 diabetes, however, this study shows that insulin pumps are a safe and effective way of controlling insulin dependent type 2 diabetes. The study is an important first step which could see the use of insulin pumps considered more widely for people with type 2 diabetes in the UK.
What's new on the forum? ⭐️
Get our free newsletters
Stay up to date with the latest news, research and breakthroughs.