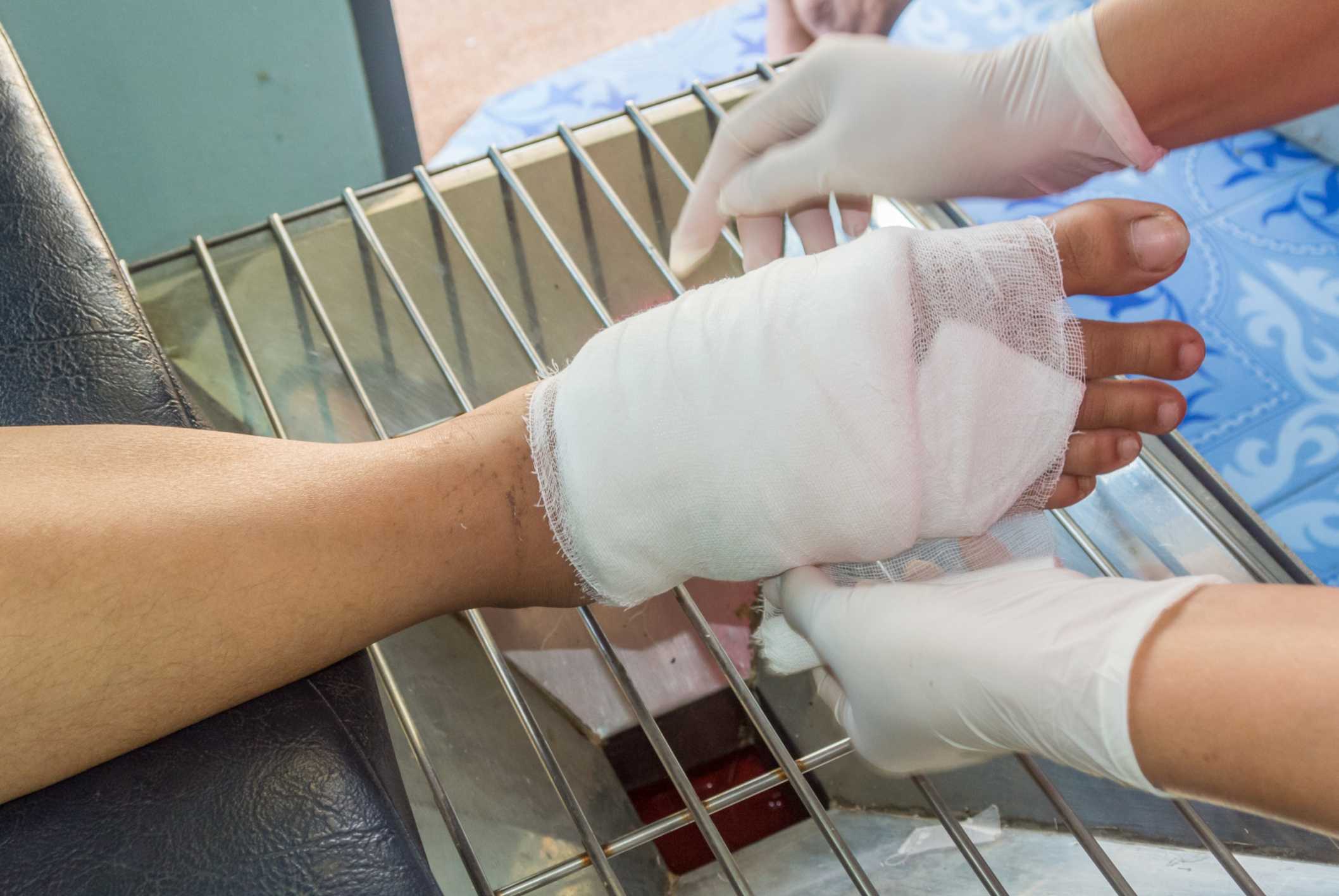
Gangrene is a state in which a certain part of the body is not getting sufficient blood circulation, causing the tissue to die.
The condition is split into two categories: Wet and Dry Gangrene.
Symptoms of gangrene
The common signs of gangrene include:
- Redness in the affected area, which can then become brown or black
- Pain evolving into numbness
Dry gangrene and diabetes
Dry gangrene is the type of gangrene that can occur as a complication of a pre-existing health condition, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes
As a result of damage to the blood vessels throughout the body due to prolonged hyperglycemia , it is possible for blood circulation to be cut off. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue around the body and so without it, the tissue will eventually die.
This usually happens in the extremities first, in the toes, feet and fingers.
Wet gangrene and diabetes
Gangrene that is caused by an infection of some sort is known as wet gangrene. It occurs after an injury that gets infected, such as a burn or frostbite.
Swelling from the body fighting off an infection can cause a loss of blood circulation that can starve a section of the body of oxygen and nutrients and cause gangrene.
This type of gangrene is more of a threat to people with diabetes who have an impaired immune system as their bodies are less able to fight off bacteria, viruses and other types of infection.
Furthermore, gangrene infections can occur at the site of foot ulcers , which is a common complication of both type 2 and type 1 diabetes
Wet gangrene is the more rapid of the two types and can lead to septic shock.
Treating gangrene
Extreme cases of gangrene may have to result in amputation , which is why it is important to be aware of the signs of gangrene so that it can be treated at an early stage.
Other methods of treating less severe cases include:
- Surgery – Gangrene can be treated via surgery by reconstructing the damaged blood vessels or bypassing them.
- Antibiotics – Antibiotic medication may be used to kill off the infection if it is caught early enough to avoid damage to the tissue.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy – Forcing oxygen into the damaged cells via a hyperbaric chamber and an oxygen hood over the damaged section stimulates healing and healthy cells.
- Maggot treatment – This has been proven to be very effective as maggots eat dead flesh and release bacteria killing secretions that help to fight the infection.