Type 2 diabetes symptoms will often develop gradually and may not always show symptoms at an earlier stage.
Type 2 diabetes symptoms can differ slightly from symptoms of type 1 diabetes
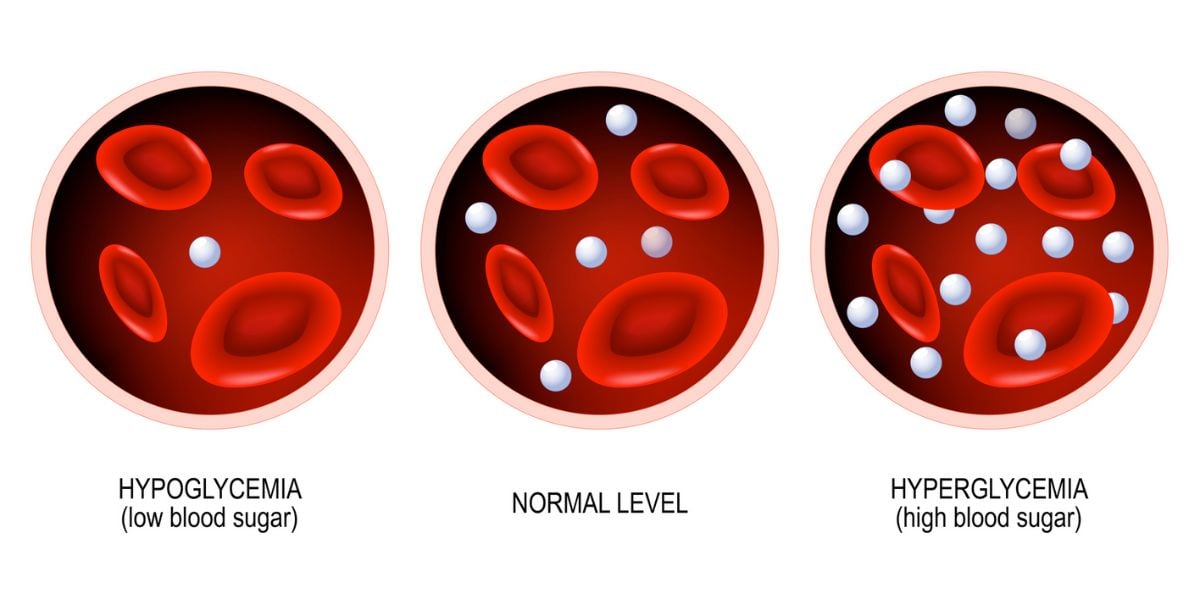
Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong condition. Once symptoms of diabetes have developed into the condition, the body will then be unable to regulate the amount of glucose in the blood.
It is important to catch the symptoms as early as possible to limit damage to the body.
Although there are 3 main diabetes signs shared by all people with diabetes, type 2 diabetes may sometimes exhibit some specific symptoms, such as certain skin disorders.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes often develops slowly, over a period of years, and the symptoms can therefore also develop gradually.
At diagnosis, people who have type 2 diabetes may show little or no symptoms of the condition.
Because the symptoms develop slowly, type 2 diabetes may commonly be diagnosed following routine medical examinations or screening tests for non-related conditions.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes may include:
- Feeling tired during the day, particularly after meals (fatigue)
- Often feeling hungry, particularly if you feel hungry shortly after eating (polyphagia)
- Urinating more often than normal, particular needing to do so during the night (polyuria)
- Feeling abnormally thirsty (polydipsia)
- Blurred vision
- Itching of the skin, particularly itchiness around the genitals (genital itchiness)
- Slow healing of cuts or wounds
- Having regular yeast infections (thrush)
- Having a skin disorder such as psoriasis or acanthosis nigricans
- Sudden weight loss or loss of muscle mass
Explore the most common symptoms of diabetes:
Common symptoms of diabetes
Spotting the symptoms of type 2 diabetes
The presence of type 2 diabetes prevents the body from being able to lower blood glucose levels as efficiently as in people without diabetes. For this reason, the symptoms of type 2 diabetes may be more noticeable following meals.
Measuring higher than normal levels of blood pressure or cholesterol may indicate a higher risk of type 2 diabetes, particularly if you are overweight and it is therefore wise to be aware of the symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
How long does it take for the symptoms of type 2 diabetes to develop?
Type 2 diabetes symptoms may be very minor for a long time, and suddenly become more serious.
This is why type 2 diabetes often goes unnoticed for many years. It is believed that up to 850,000 adults could have type 2 diabetes and be unaware of it
It’s important not to disregard the symptoms of diabetes as being down to getting older.
Catching the symptoms early
It is important to catch the symptoms early so that the damage caused by type 2 damage is limited.
If type 2 diabetes is caught at a later stage, some of the complications may be present at diagnosis, such as:
Type 2 diabetes can also lead to a significant loss of the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This is referred to beta cell turnover.
Catching and treating type 2 diabetes early can help to prevent a significant loss of insulin producing cells, which may help to prevent or delay a need to take insulin injections.
Can I reverse type 2 diabetes?
The body is indeed able to ‘reverse’ or put type 2 diabetes into remission. This is acheived by reducing HbA1c to under the diagnosis threshold. However, unhealthy habits can cause this to relapse.